Carbon dioxide can be turned into gasoline?
Can carbon dioxide, which is common in the air, be made directly into gasoline, diesel or liquefied petroleum gas? Chinese scientists say yes.
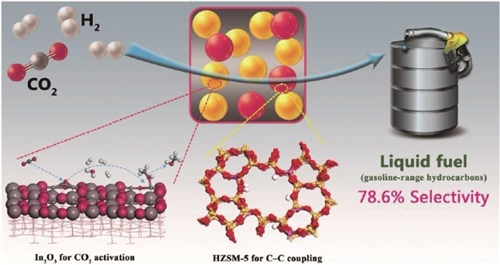
Recently, low-carbon transformation of science and engineering of the Chinese Academy of Sciences key laboratory of Shanghai institute of Shanghai university of science and technology, high low carbon energy lab in the field of carbon dioxide (CO2) using the significant progress, creatively using indium oxide/molecular sieve bifunctional catalyst, realized the high selectivity for CO2 step into liquid fuel (gasoline of high carbon hydrocarbons). The research results were recently published online in the journal Nature Chemistry, and have been applied for a Chinese invention patent and an international PCT patent.
turn CO2 into gasoline
Why turn CO2 into gasoline?
Due to the increasing demand for energy, the consumption of fossil fuels and total CO2 emissions are rising rapidly, while the large-scale use of alternative energy (solar energy, wind energy, etc.) is limited by its inherent intermittency, volatility and randomness. Hydrocarbons such as gasoline and aviation kerosene are important liquid transportation fuels, which are widely used in the world and have high economic value. Nobel Prize-winning chemistry professor Ola has developed the concept of an "artificial carbon cycle", which could be made efficient by converting CO2 directly into liquid fuels with alternative energy sources.
So by converting CO2 into a useful chemical or fuel using hydrogen, which is produced by electrolysis of water from renewable energy sources, scientists can kill three birds with one stone -- helping to solve environmental problems caused by increased CO2 concentrations in the atmosphere, over-reliance on fossil fuels and the storage of renewable energy.
At present, the research on CO2 resource utilization mainly focuses on the synthesis of simple carbon one (C1) molecular compounds such as methanol, formic acid and methane. Due to the chemical inertia of CO2 molecule and the kinetic obstacle formed by C-C bond, it is still a huge challenge to convert it into products containing two or more carbon atoms.
For a long time, due to the lack of effective catalyst system, the direct synthesis of high carbon hydrocarbons from CO2 is less studied. Existing studies on the synthesis of high carbon hydrocarbons from CO2 mainly focus on the modified iron-based Fischer Tropsch catalyst, and the by-product methane is usually greater than 6%. The Key Laboratory of Low Carbon Conversion Science and Engineering of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has successfully designed In2O3/HZSM-5 bifunctional catalyst by effectively coupling C=O bond activation with C -- C bond coupling function, making a breakthrough in the highly selective conversion of CO2 to high-carbon hydrocarbons. Among the hydrocarbon products, the selectivity of hydrocarbon components (C5 to C11) of gasoline is up to nearly 80%, while that of CH4 is less than 1%. In addition, the team has scaled up the catalyst preparation to produce industrial-size granular catalysts with high mechanical strength, and the catalyst system is ready for demonstration in industrial conditions.
In addition to gasoline hydrocarbon components, CO2 can be directly converted to liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) and even diesel oil with high selectivity by adjusting the pore size of the catalyst system.
The work was highly praised by Nature Chemistry reviewers as a breakthrough in the field of CO2 conversion, providing an important platform for the conversion of CO2 to chemicals and fuels.




 Facebook
Facebook YouTube
YouTube LinkedIn
LinkedIn Twitter
Twitter