Harm of exceeding SO2 in food (2)
Sulfur dioxide can be toxic in excess
Sulfite is produced after sulfur dioxide enters the body, and is oxidized to sulfate by sulfite oxidase in tissue cells. After normal detoxification, it is finally discharged from the body in the urine. Therefore, a small amount of sulfur dioxide entering the body can be considered safe and harmless. Its toxicity mainly manifested as the acute and chronic harm caused by occupational exposure.
Acute poisoning can cause eye, nose, mucous membrane to stimulate symptom, produce laryngeal spasm, laryngeal oedema, bronchospasm when serious, a large number of inhalation can cause pulmonary oedema, asphyxia, coma and even death. The human olfactory threshold of sulfur dioxide in the air is 0.03mg/L, the stimulation threshold is 0.01mg/L, 0.03mg/L can only tolerate 1 minute.
Chronic toxicity Long-term exposure to small doses of sulfur dioxide in the air can lead to a dulled sense of smell, chronic rhinitis, bronchitis, and decreased pulmonary ventilation and immune function. In severe cases, it can cause diffuse pulmonary interstitial fibrosis and toxic pulmonary hardening. The main toxic manifestations of oral intake of SO2 are gastrointestinal reactions, such as nausea and vomiting. In addition, can affect calcium absorption, promote the body calcium loss.
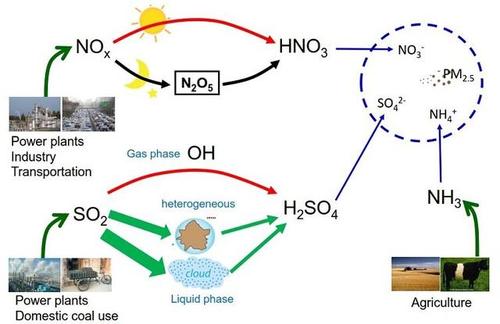
Chemical cycles of SO2, NOx, and NH3 in the atmosphere
Sulfur dioxide service standard
In order to ensure the health of consumers, China has stipulated in the food additive standard the use range, usage amount and the maximum residual amount of sulfur dioxide in food. For example, sulfur is limited to fumigating preserves, dried fruits, dried vegetables, vermicellas and sugar; Sodium hyposulfite can be used for preserves, dried fruits, dried vegetables, vermicelli, glucose, sugar, rock sugar, caramel, candies, liquid glucose, bamboo shoots, mushrooms and canned mushrooms, the maximum usage is 0.40g/kg; The maximum amount of SO2 that can be used in wine, fruit wine, etc., should not exceed 0.25g/kg. Bamboo shoots, candied fruit, mushrooms and canned mushrooms, grapes, wine and fruit wine should not exceed 0.05g/kg of sulfur dioxide residue. Biscuits, sugar and vermicelli residues should not exceed 0.1g/kg. The risk assessment of SO2 as food additives by the Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) of FAO and WHO is as follows: the ADI of SO2 is 0 ~ 0.7mg/ kg body weight, that is, the daily intake of SO2 should not exceed 42mg for a 60kg adult.
If not grasp the sulfur dioxide in the process of food processing class material usage, or some enterprise in order to pursue its product has good appearance color or extend food parcel or to cover up the bad food, regardless of the standard limit, excessive use of sulfur dioxide additives, is likely to cause more than the national standard of sulfur dioxide residues in food, which caused a certain adverse effect to human body health.
- Prev: Separation Of Isotope Gases
- Next: What is the NO2 ?




 Facebook
Facebook YouTube
YouTube LinkedIn
LinkedIn Twitter
Twitter