History of liquid helium preparation (part 3)
Heliumis normally a colorless, odorless gas. Melting point -272.2℃ (25 atmospheric pressure), boiling point -268.785℃; Density 0.1785 g/l, critical temperature -267.8℃, critical pressure 2.26 atmospheres; Solubility in water is 8.61 cm/kg water. Helium is the only material that does not solidify at standard atmospheric pressure. Liquid helium in the temperature dropped to 2.18 K (He Ⅱ), the nature of the mutations, become a superfluid, can flow upward along the container wall, the thermal conductivity of copper, 800 times and turn it into a superconductor; Its specific heat capacity, surface tension and compressibility are all abnormal.
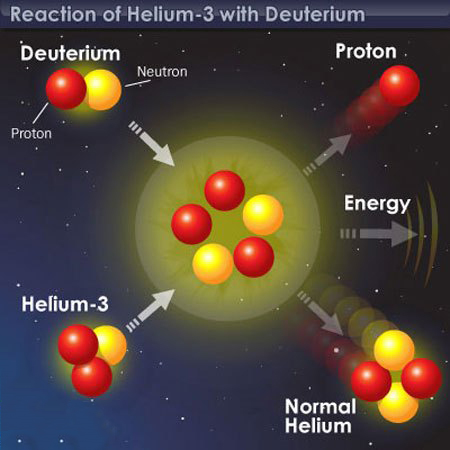
Reaction of Helium-3 with Deuterium
Liquid helium has a density of 0.125 g/mL at one atmosphere. Helium comes in two natural isotopes: helium 3 and helium 4, and almost all of the helium found in nature is helium 4
Helium transforms from gaseous helium to liquid helium at extremely low temperatures. Because of the interaction between helium atoms (the Van der Waals force) and the atomic mass is very small, it is difficult to liquefy and harder to solidify. The critical temperature and critical pressure intensity of the gas-liquid transformation curve of rich isotope 4He are 5.20K and 2.26 atmospheric pressure respectively, and the temperature at one standard atmospheric pressure is 4.215K. At atmospheric pressure, when the temperature drops from the critical temperature to absolute zero, helium remains liquid all the time, does not solidify, and only becomes solid at pressures greater than 25 atmospheres.
In 1873, van der Waals, in his doctoral thesis on the Continuity of Liquid and Gas, proposed the "equation of state of matter" including gas and liquid, demonstrated that gas and liquid energy transform each other in a continuous way, and pointed out that there is a critical temperature in all gases, which has become the theoretical guidance for all gas liquefication in the future. Van der Waals also suggested that molecules not only take up volume but also act on each other.
In 1880 Van der Waals came up with the law of correspondence, which described the behaviour of all gases in a single equation. Guided by van der Waals's law of correspondence, James Dewar liquefied hydrogen in 1898, and Kamerlin-Onnes liquefied helium in 1908.
History of liquid helium preparation (part 1)




 Facebook
Facebook YouTube
YouTube LinkedIn
LinkedIn Twitter
Twitter